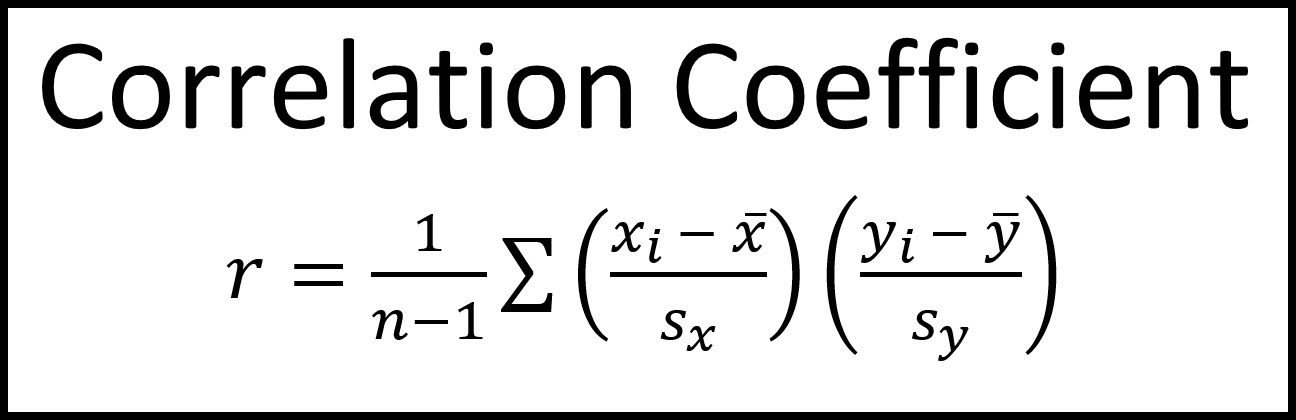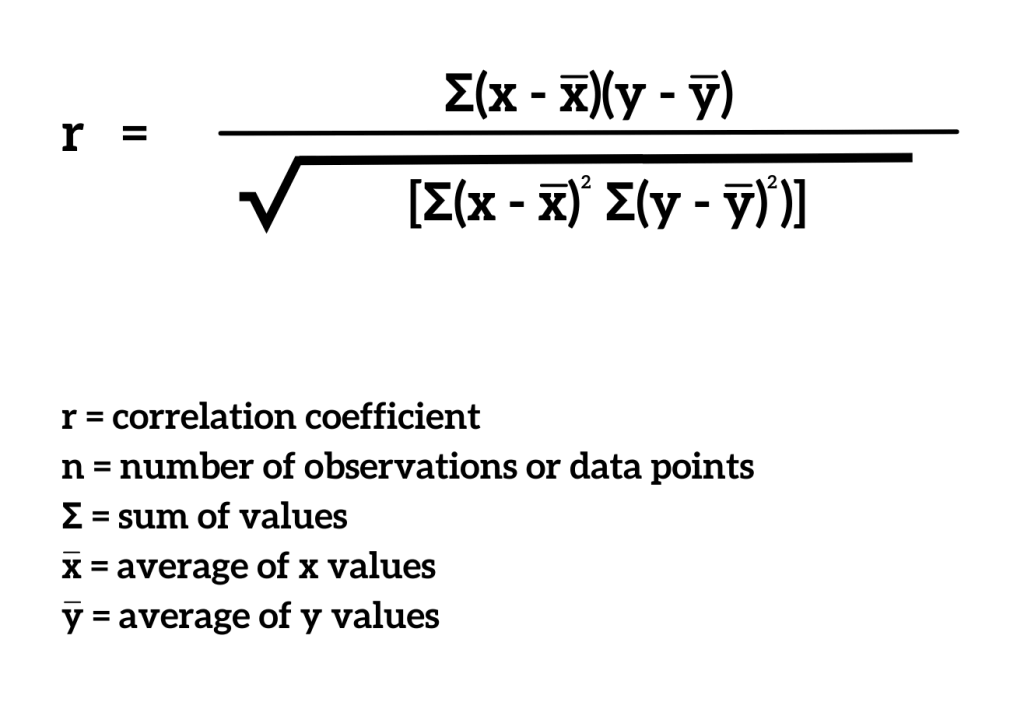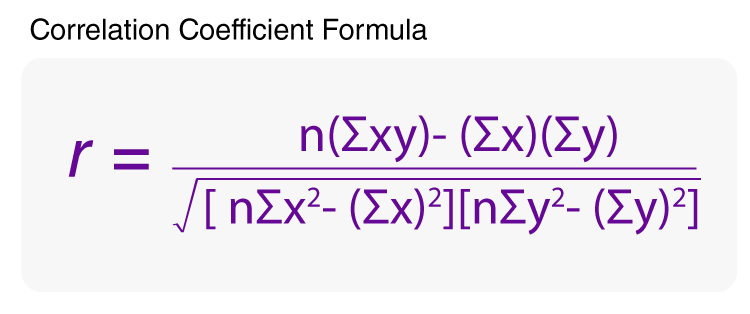Have you ever wondered how data scientists and researchers understand the relationships between different variables? What is a correlation coefficient, and why does it matter so much in uncovering hidden patterns in everything from market trends to scientific studies? This comprehensive article dives deep into the fascinating world of statistical relationships, explaining not just what a correlation coefficient is, but also why its a cornerstone of data analysis. Well explore its types, how to interpret its values, and when you should—and shouldnt—rely on it. Get ready to demystify this powerful statistical tool, understand its practical applications in real-world scenarios, and gain the confidence to interpret data relationships like a pro. This guide will empower you to look beyond surface-level observations and grasp the deeper connections within your data, making complex concepts accessible and engaging for everyone curious about the invisible threads that tie information together.
What is a correlation coefficient, and how does this powerful number help us truly understand the intricate web of relationships in the world around us? Every single day, were bombarded with countless pieces of information, and our minds naturally try to connect the dots: Does dedicating more hours to studying genuinely lead to better academic performance? Does a significant increase in advertising spending reliably translate into a boost in company sales? This little number, the correlation coefficient, steps in to provide a precise, quantifiable, and objective answer to such pivotal questions, telling us not only how strongly but also in what direction two different things tend to move together. It’s an absolutely fundamental analytical tool for anyone and everyone — from curious high school students embarking on their first science project to seasoned data scientists sifting through complex market data — who wants to move beyond mere assumptions and truly grasp the underlying connections and dynamics in data. This understanding gives us the incredible power to make more informed decisions, to predict outcomes with greater accuracy, and ultimately, to unveil the hidden patterns and dynamics that shape various phenomena, turning raw information into insightful knowledge that empowers us to navigate our data-rich environment with confidence.
Ever felt overwhelmed by a pile of numbers, wondering if there’s any real story lurking within them? Its a common feeling, isnt it? We live in an age awash with data, and making sense of it can often feel like searching for a needle in a haystack. But what if there was a simple, elegant way to uncover the invisible threads that connect different pieces of information? What if you could easily quantify whether two things tend to rise and fall together, or if one generally goes up while the other goes down? This is precisely where the concept of what is a correlation coefficient steps in, transforming a mountain of raw data into understandable insights. This article aims to pull back the curtain on this indispensable statistical measure, explaining not only its fundamental definition but also why it holds such immense importance in fields ranging from scientific research to everyday business decisions. We’ll empower you with the knowledge to interpret these coefficients confidently, helping you unlock the deeper stories hidden within any dataset and make more sense of the patterns that shape our world, ultimately turning complex data into clear, actionable understanding for anyone who seeks it.
What is Correlation Coefficient? Unveiling Its Core Definition
What is a Correlation Coefficient? Understanding the Basics
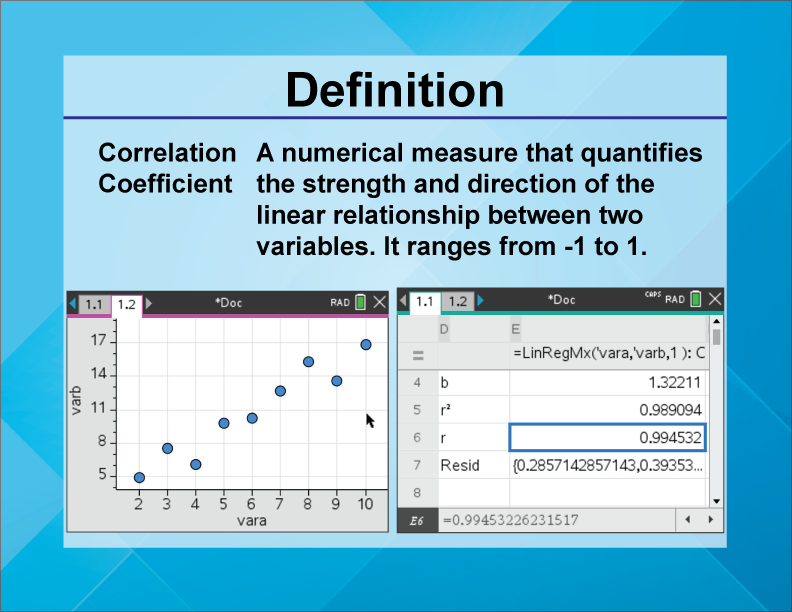
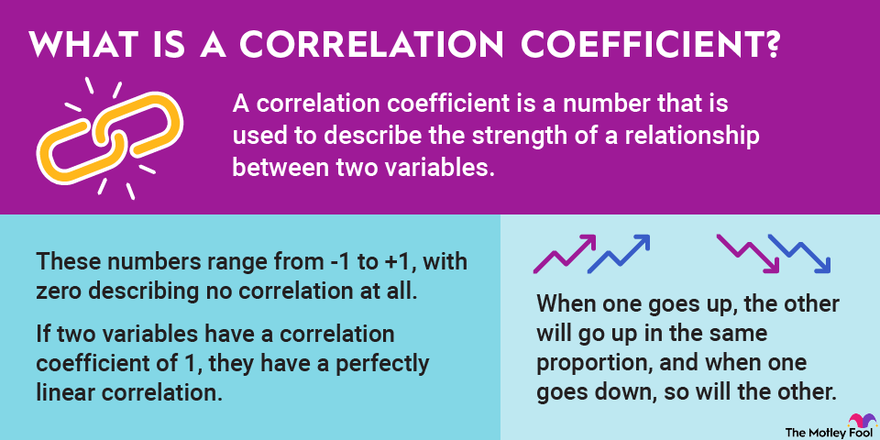
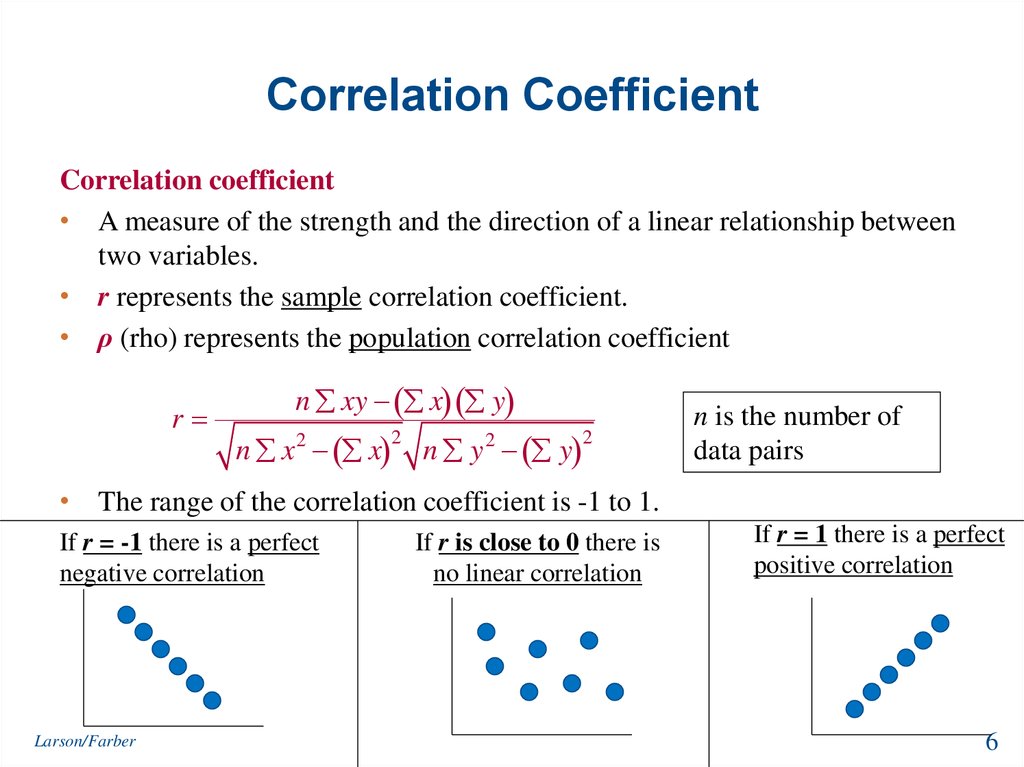
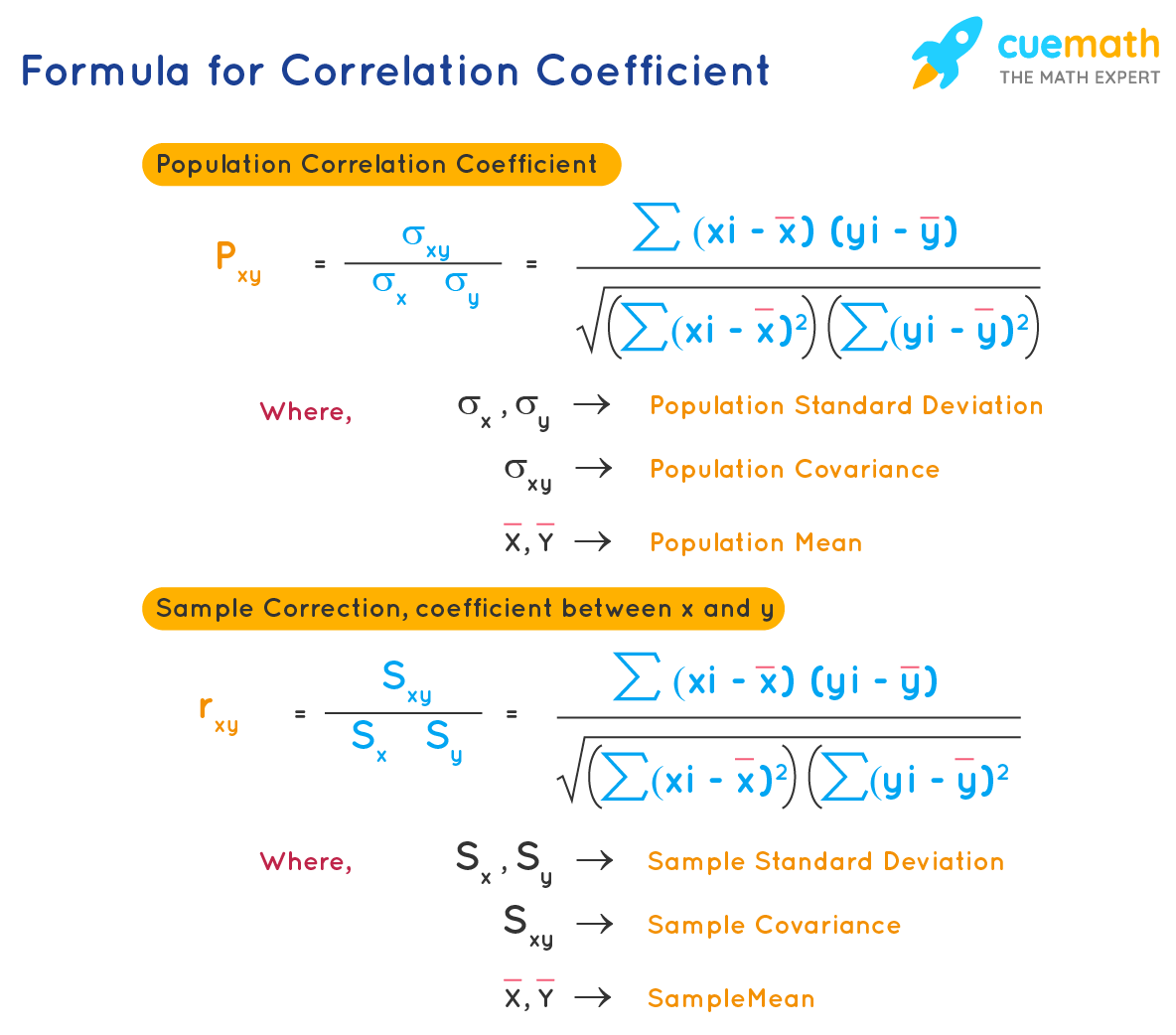
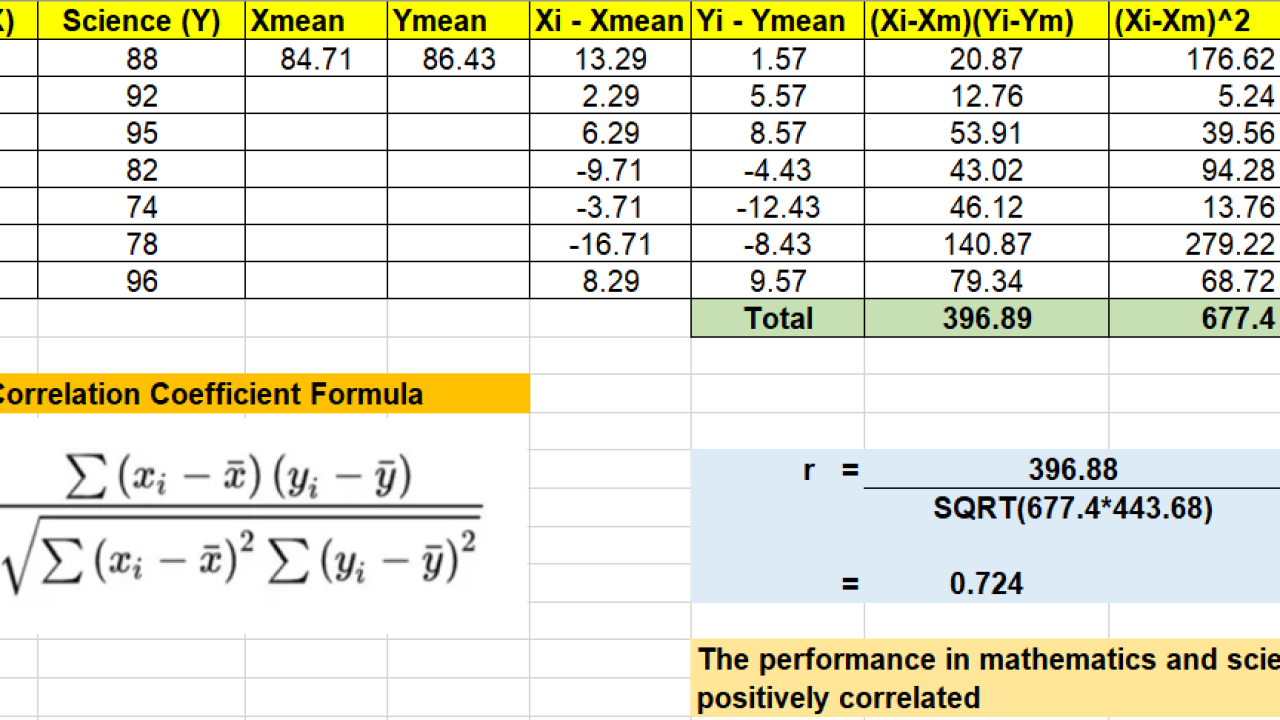
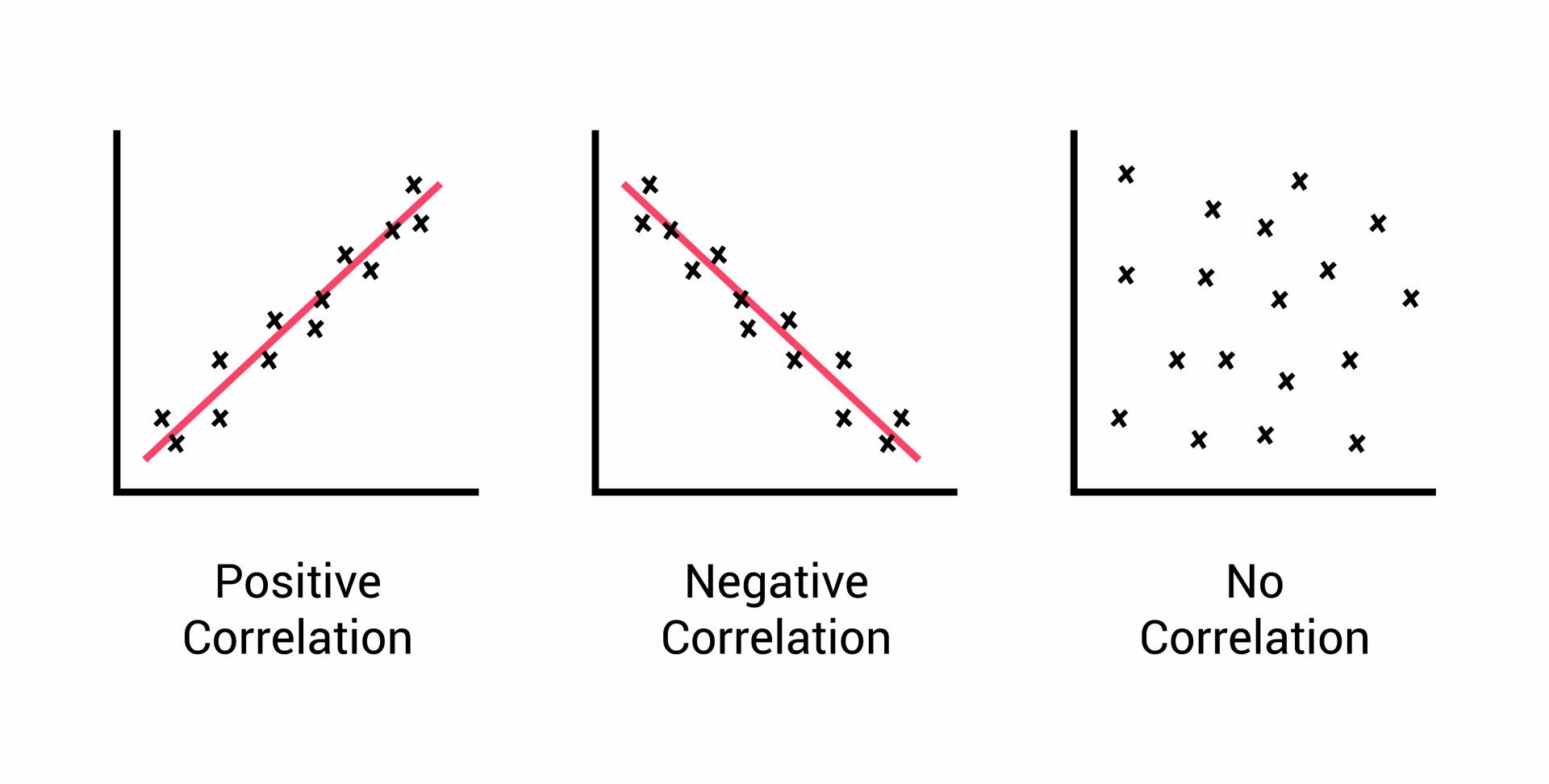
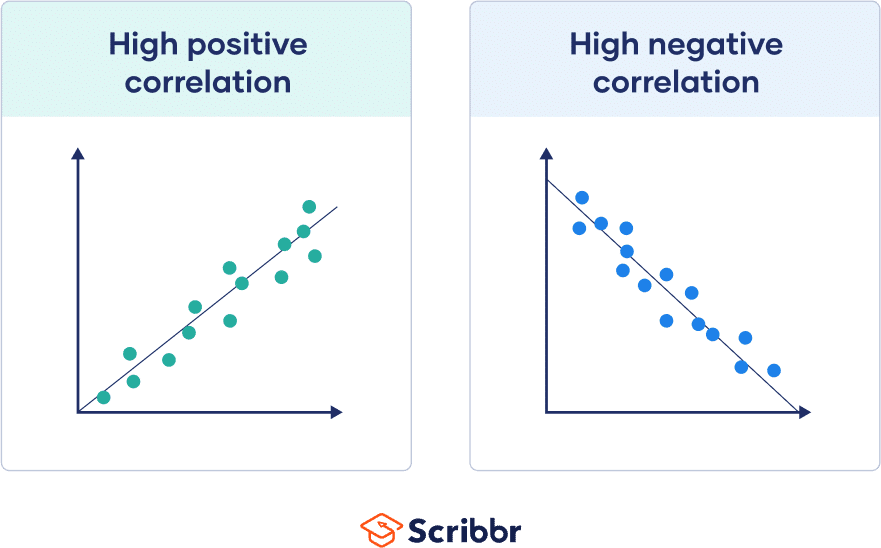
So, what exactly is a correlation coefficient? At its heart, a correlation coefficient is a single, standardized number that tells us two crucial things about the linear relationship between two variables: its strength and its direction. Imagine youre observing two trends, like how many hours someone studies and their exam score. Do they typically increase together? Or does one tend to go up while the other goes down? The correlation coefficient answers this by boiling down complex data points into a straightforward numerical value that usually ranges from -1 to +1. When we talk about strength, we mean how consistently these two variables move together; a strong relationship means they follow a similar pattern very closely, while a weak one suggests their movements are more independent or scattered. The direction indicates whether they move in the same way (positive correlation) or in opposite ways (negative correlation). Why is this so important? Because it allows us to quantify an observable relationship objectively, moving beyond mere anecdotal evidence and providing a solid foundation for further analysis or even prediction. Understanding this core definition is the first step toward grasping its profound utility in almost every field that deals with quantitative data, from economic forecasting to medical research, providing clarity where there might otherwise be only speculation.
What is Correlation Coefficient? Exploring Its Range and Interpretation
How Does the Correlation Coefficient Work? Decoding the Numbers
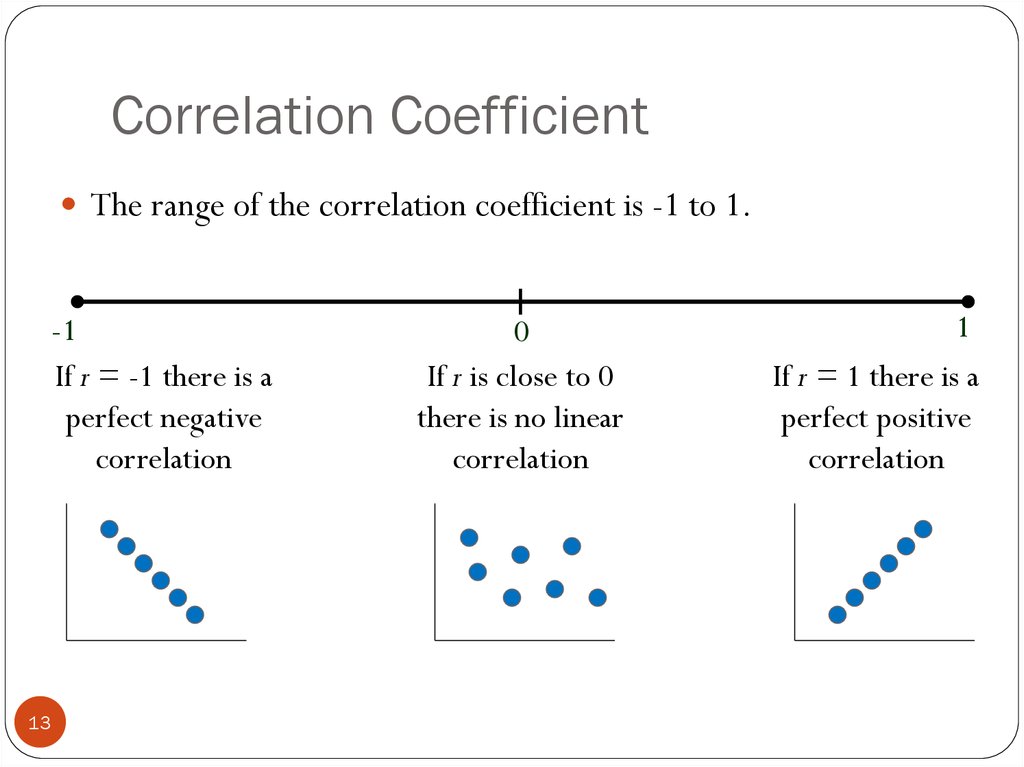
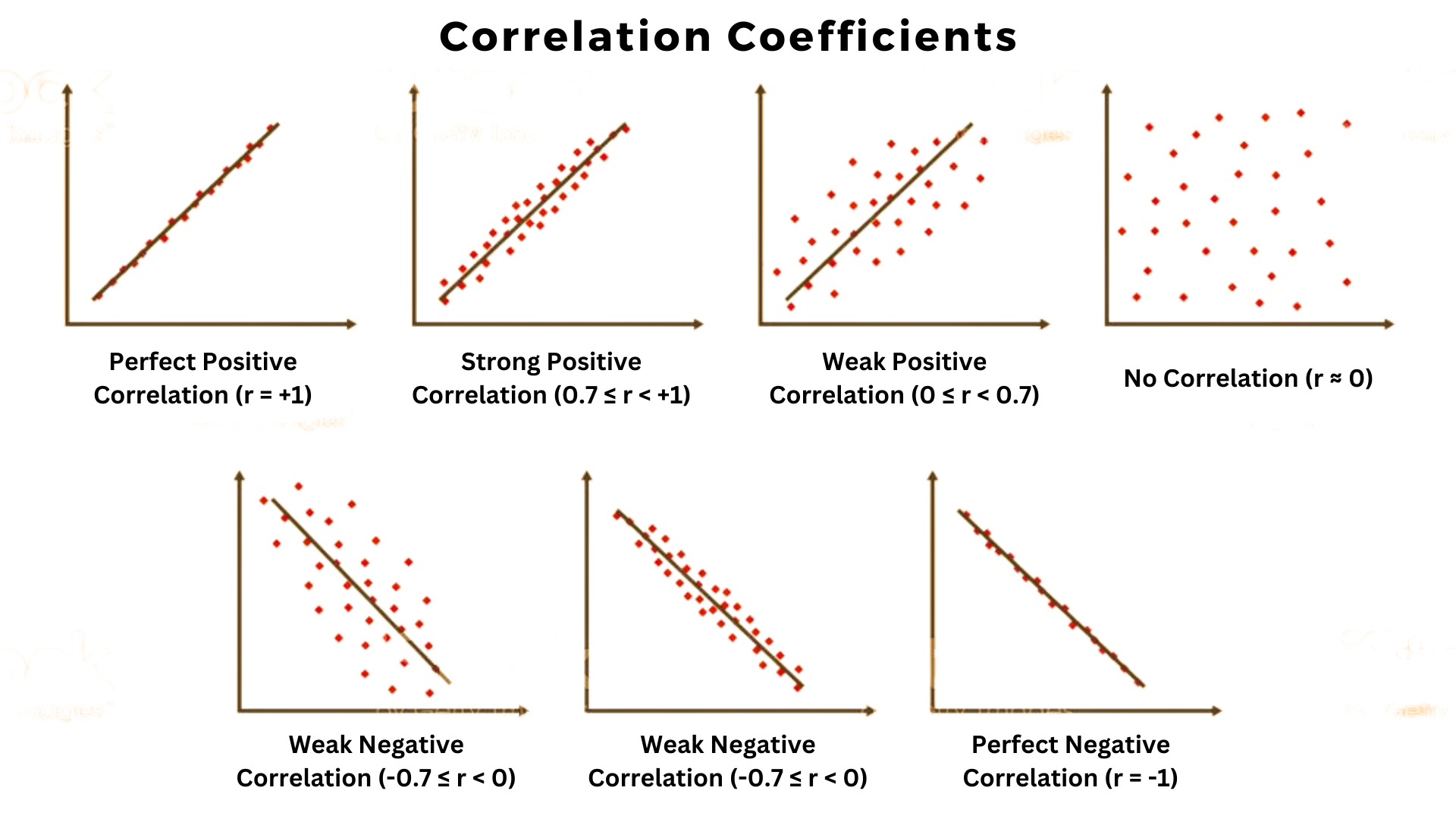
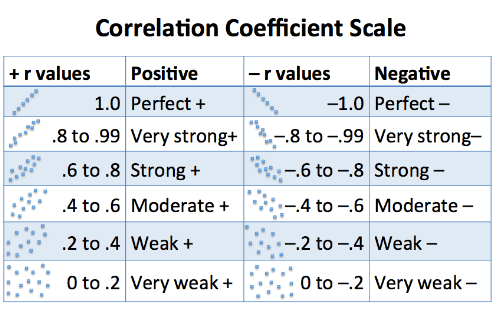
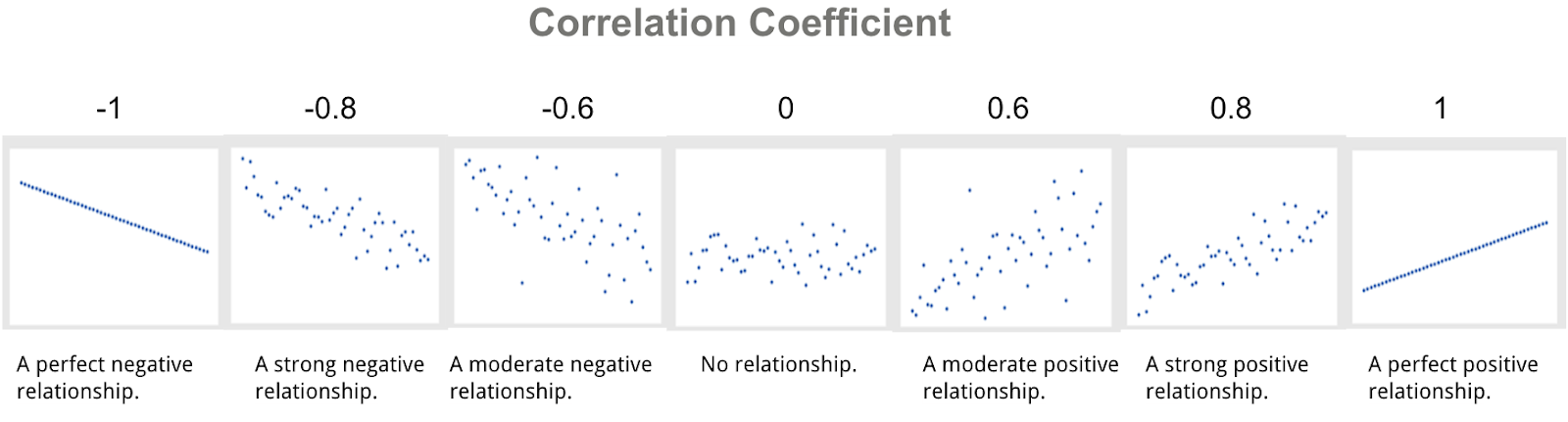
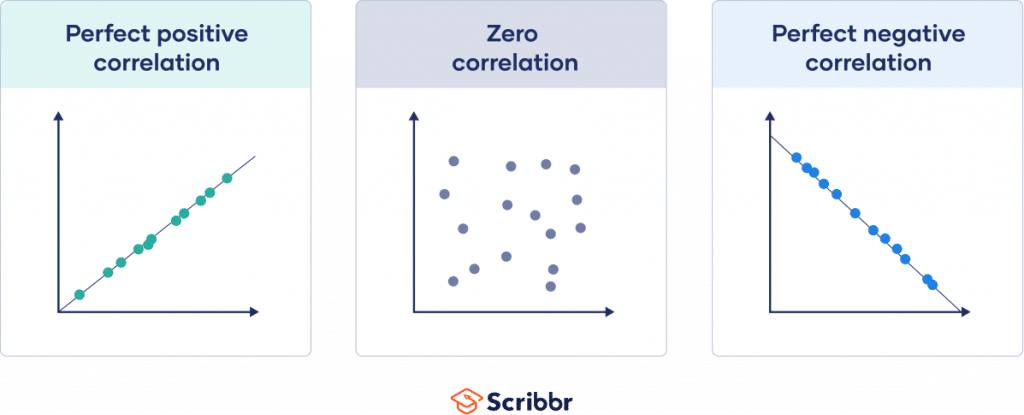
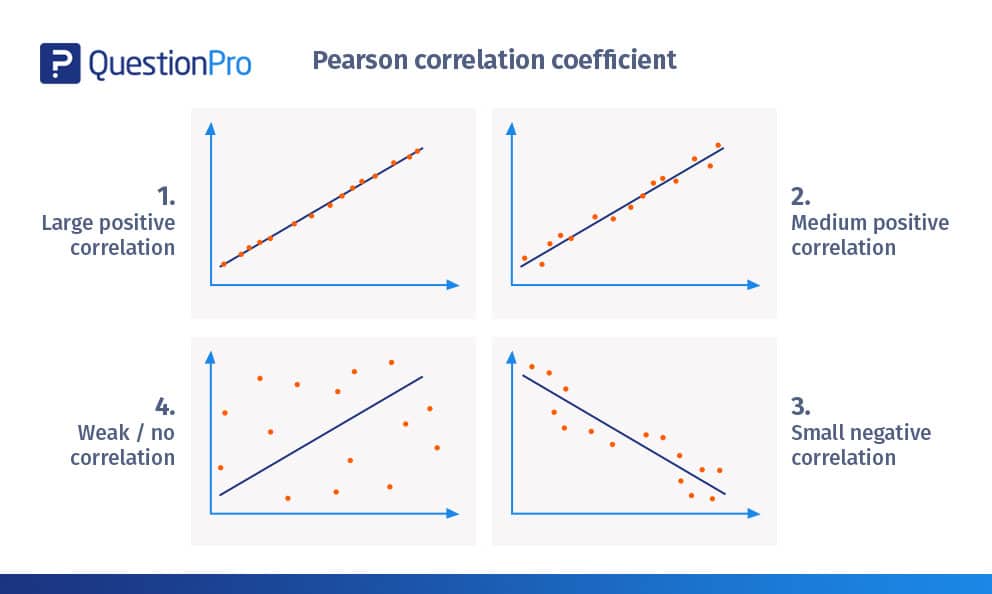
Once we understand what a correlation coefficient is, the next vital step is to decipher its numerical language. This powerful statistical measure always falls within a specific range, from -1.0 to +1.0, and each position within this spectrum carries significant meaning. Let’s break down what these numbers truly represent. A coefficient of +1.0 indicates a perfect positive linear correlation, meaning that as one variable increases, the other variable increases proportionally and perfectly, without any deviation. Think about the relationship between the number of hours you work and the money you earn, assuming a fixed hourly wage; they move in lockstep. Conversely, a coefficient of -1.0 signifies a perfect negative linear correlation, where as one variable increases, the other decreases proportionally and perfectly. Imagine, for example, the relationship between the number of people remaining on a train and the number of stops it has made from its origin; as stops increase, passengers decrease. When the coefficient is 0, it means there is no linear relationship between the two variables at all; their movements appear completely unrelated or random. Numbers between 0 and +1.0 indicate varying degrees of positive correlation, with values closer to +1.0 showing a stronger positive link, while numbers between 0 and -1.0 suggest varying degrees of negative correlation, with values closer to -1.0 indicating a stronger negative connection. Why is this range so crucial? It provides a universal benchmark, allowing researchers across different disciplines to compare relationships objectively and draw consistent conclusions about how different phenomena interact within our complex world, offering a clear lens through which to view statistical connections and their implications.
What is Correlation Coefficient? Types and Their Applications
What are the Different Types of Correlation Coefficients?
While the concept of what is a correlation coefficient is generally about measuring relationships, several types exist, each tailored to specific data characteristics and research questions. When do we use which type, and why does it matter? The most commonly encountered and widely recognized is the Pearson Product-Moment Correlation Coefficient, often simply called Pearsons r. This coefficient is specifically designed to measure the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two continuous variables. It works best when your data points tend to fall along a straight line. For instance, if youre exploring the relationship between a persons height and their weight, Pearsons r would be an excellent choice, assuming this relationship is generally linear. However, what happens when the relationship isnt strictly linear but still shows a consistent trend, perhaps curved or increasing but not at a constant rate? This is where other coefficients, like Spearmans Rank Correlation Coefficient (Spearmans rho), become incredibly valuable. Spearmans rho measures the strength and direction of a monotonic relationship between two ranked variables, meaning that as one variable increases, the other tends to either increase or decrease, but not necessarily at a constant rate. Its particularly useful for ordinal data or when the underlying assumptions for Pearsons r (like normality) are not met. For example, if youre looking at the relationship between students rankings in a math competition and their rankings in a science competition, Spearmans rho would be more appropriate. Knowing which coefficient to apply is vital because using the wrong one can lead to inaccurate conclusions about the nature of your datas relationships, providing a robust framework for selecting the right tool for the right analytical job and ensuring your findings are both valid and meaningful in their context.
| Coefficient Value | Strength of Linear Relationship | Direction of Relationship | Interpretation Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| +1.0 | Perfectly Strong | Positive | Hours worked and earnings (fixed wage) |
| +0.7 to +0.9 | Very Strong | Positive | Education level and income |
| +0.4 to +0.6 | Moderate | Positive | Ice cream sales and temperature |
| +0.1 to +0.3 | Weak | Positive | Shoe size and IQ |
| 0 | None (linear) | No Direction | Phone number digits and height |
| -0.1 to -0.3 | Weak | Negative | Number of cigarettes smoked and lung capacity |
| -0.4 to -0.6 | Moderate | Negative | Car age and resale value |
| -0.7 to -0.9 | Very Strong | Negative | Amount of exercise and body fat percentage |
| -1.0 | Perfectly Strong | Negative | Fuel in tank and distance traveled (after filling) |
What is Correlation Coefficient? Why It Matters in Real Life
Why is Understanding the Correlation Coefficient Important?
So, we know what a correlation coefficient is and how to read its values, but why should any of this matter to us in our daily lives or professional pursuits? The true power of this statistical measure lies in its ability to inform decision-making, identify potential relationships, and even drive innovation across countless fields. Where do we see its impact? Businesses use it to understand market trends, for instance, correlating advertising spend with sales figures to optimize their marketing strategies. Healthcare professionals might analyze the correlation between specific lifestyle factors and disease incidence, helping to guide public health initiatives and patient advice. Researchers in social sciences use it to explore the relationships between different social phenomena, like education levels and voting patterns. When you understand what is a correlation coefficient, you gain a vital lens through which to view the world, allowing you to move beyond gut feelings and into evidence-based reasoning. It empowers you to ask better questions about data, to challenge assumptions, and to identify areas where further investigation is warranted. However, it’s crucial to remember a golden rule: correlation does not imply causation. Just because two variables move together doesnt mean one causes the other. For example, ice cream sales and drowning incidents often show a positive correlation, but neither causes the other; both are influenced by a third factor: warm weather. Despite this important caveat, the correlation coefficient remains an indispensable tool for initial data exploration, hypothesis generation, and making smarter, more informed choices in a data-driven world, offering a clear path to understanding complex dynamics and fostering informed action.
What is Correlation Coefficient? Common Pitfalls and Best Practices
How to Use Correlation Coefficients Effectively? Avoiding Misinterpretations
While understanding what is a correlation coefficient provides immense analytical power, its equally important to be aware of its limitations and best practices to avoid common misinterpretations. How can we ensure were using this tool wisely and not drawing faulty conclusions? The most significant pitfall, as mentioned, is mistaking correlation for causation. Just imagine finding a strong positive correlation between the number of storks nesting in a region and the birth rate in that same region. Does that mean storks deliver babies? Of course not! Both might simply be correlated with a third factor, like rural population density or warmer climates. Therefore, always approach correlational findings with a healthy dose of skepticism and look for other evidence before assuming a causal link. Another common mistake involves outliers. Extreme values in your data set, known as outliers, can dramatically skew the correlation coefficient, making a weak relationship appear strong or vice versa. It’s always a good practice to visualize your data using scatter plots before calculating the coefficient to identify any potential outliers or non-linear patterns that the Pearson coefficient might misrepresent. Furthermore, be mindful of the range of your data; a strong correlation observed over a narrow range might not hold true over a wider range. Always consider the context and the nature of your variables. By understanding these nuances and adopting best practices like data visualization and critical thinking, you can harness the true potential of what is a correlation coefficient, ensuring your interpretations are robust, accurate, and truly insightful, empowering you to navigate the complexities of data analysis with confidence and precision.
Summary Q&A: What is a Correlation Coefficient?
What exactly is a correlation coefficient, and what purpose does it serve in data analysis? At its core, it’s a robust numerical measure, almost always falling within a range from -1.0 to +1.0, explicitly designed to quantify both the strength and the direction of a linear relationship that exists between any two given variables. Think of it as a statistical flashlight that illuminates how two things move in tandem, or in opposition, within your data.
Why is understanding this statistical concept so incredibly important for professionals and everyday curious minds alike? Its importance cannot be overstated, as it serves as a critical compass, helping us to clearly understand how different factors relate to each other across virtually all domains. This knowledge is paramount for informing strategic decisions, making accurate predictions, and identifying meaningful trends in fields spanning from cutting-edge scientific research to astute business analytics and even public policy debates, offering a profound lens on interconnectedness.
How do we confidently interpret the various values that a correlation coefficient can take on? Interpreting its values is quite straightforward once you grasp the basics: values that are remarkably close to +1.0 consistently indicate a very strong and direct positive relationship, meaning as one variable increases, the other reliably increases too. Conversely, values that hover near -1.0 signify an equally strong but inverse negative relationship, where an increase in one variable corresponds to a decrease in the other. If the value hovers around 0, it compellingly suggests there is no discernible linear relationship between the two variables whatsoever.
What are the main types of correlation coefficients researchers and analysts commonly employ, and when should each be used? The two most widely recognized and utilized types are Pearson’s r, which is expertly suited for measuring linear relationships between continuous variables, and Spearman’s rho, which is particularly effective for analyzing monotonic relationships, often employed with ranked or ordinal data, providing flexibility for different data structures.
What is the single most crucial caution or limitation to remember when working with correlation coefficients to avoid drawing faulty conclusions? The absolute key caution, a principle that cannot be stressed enough, is the powerful mantra that correlation emphatically does not imply causation. Just because two things demonstrate a strong relationship doesnt inherently mean that one causes the other to occur. Always remember to seek additional evidence and context before jumping to causal conclusions.
A correlation coefficient measures the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two variables. Its value ranges from -1 to +1, where -1 indicates a perfect negative correlation, +1 indicates a perfect positive correlation, and 0 indicates no linear correlation. Common types include Pearson (for linear relationships) and Spearman (for monotonic relationships, including non-linear). Understanding correlation is crucial for making informed decisions, predicting trends, and identifying potential causal links (though correlation does not imply causation). Interpreting its value helps in assessing the significance and practical implications of observed relationships in various fields.
What Is A Coefficient Correlation Formula US Cfa Calculate Correlation At Ellen Martinez Blog Img 23 Correlation Coefficient Graph Svg Correlation Coefficient 880
Correlation Coefficient Education Formal Education Correlation What Is Correlation Coefficient And Its Types Infoupdate Org Correlation What Is Correlation Coefficient And Its Types Infoupdate Org Pearson Correlation Coefficient 1 Correlation Coefficient What It Is Formulas Examples What Is Correlation Coefficient
Coefficient Example Sddefault Correlation Coefficient Definition Types And Examples Graph The Correlation Coefficient YouTube Correlation Coefficient Slide 11
Correlation Coefficient 8th Grade Flashcard Wayground D2026c68 Fe4f 4baf 94edCorrelation Coefficient Types Formulas Examples 01 Correlation Types 1024x415 Correlation Coefficient What Is It Formula Correlation Coefficient Video Definition 26 Linear Function Concepts Correlation Coefficient Defintion
Correlation Coefficient Formula What Is The Correlation Coefficient Correlation Coefficient Formula 1612436633 1623057264 Correlation Coefficient Slide 12 Correlation Coefficient Formula Pearson Correlation Coefficient Example 1280x720 Correlation Coefficient Graph Svg Ogimage
What Is Correlation And The Correlation Coefficient YouTube Positive Correlation Definition And What Is Correlation Correlation Coefficient The Scale Of Pearsons Correlation Coefficient Analysis Ppt Download Correlation
Correlation Coefficient Types Formulas Examples High Correlation Correlation Coefficient Correlation Coefficient The Linear Correlation Coefficient YouTube How To Do Linear Regression And Correlation Analysis 2c4dd36d Ef1e 45af 8499 1600x431
The Correlation Coefficient A Guide For Non Experts Correlation Coefficient 1024x702 Correlation Correlation Coefficient Types Formulas Example Correlation Correlation Coefficient Formula Calculation With Excel Template Correlation Coefficient Formula What Is Correlation Coefficient And Its Types Infoupdate Org Correlation Coefficient Formula
Correlation Coefficient Slide 5 Pearson Correlation Definition At Brooke Fitzroy Blog Correlation Coefficient Correlation Coefficient How To Calculate Using Formula Minitab Burgundy Hotel Restaurant Food YouTube Thumbnail 1 1024x576 Correlation Coefficient Definition Definition